In FCFS Scheduling,
- The process which arrives first in the ready queue is firstly assigned the CPU.
- In case of a tie, process with smaller process id is executed first.
- It is always non-preemptive in nature.
Advantages-
- It is simple and easy to understand.
- It can be easily implemented using queue data structure.
- It does not lead to starvation.
Disadvantages-
- It does not consider the priority or burst time of the processes.
- It suffers from convoy effect.
Convoy Effect
In convoy effect,
|
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON FCFS SCHEDULING-
Problem-01:
Consider the set of 5 processes whose arrival time and burst time are given below-
| Process Id | Arrival time | Burst time |
| P1 | 3 | 4 |
| P2 | 5 | 3 |
| P3 | 0 | 2 |
| P4 | 5 | 1 |
| P5 | 4 | 3 |
If the CPU scheduling policy is FCFS, calculate the average waiting time and average turn around time.
Solution-
Gantt Chart-
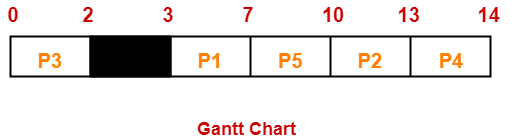
Here, black box represents the idle time of CPU.
Now, we know-
- Turn Around time = Exit time – Arrival time
- Waiting time = Turn Around time – Burst time
| Process Id | Exit time | Turn Around time | Waiting time |
| P1 | 7 | 7 – 3 = 4 | 4 – 4 = 0 |
| P2 | 13 | 13 – 5 = 8 | 8 – 3 = 5 |
| P3 | 2 | 2 – 0 = 2 | 2 – 2 = 0 |
| P4 | 14 | 14 – 5 = 9 | 9 – 1 = 8 |
| P5 | 10 | 10 – 4 = 6 | 6 – 3 = 3 |
Now,
- Average Turn Around time = (4 + 8 + 2 + 9 + 6) / 5 = 29 / 5 = 5.8 unit
- Average waiting time = (0 + 5 + 0 + 8 + 3) / 5 = 16 / 5 = 3.2 unit
Problem-02:
Consider the set of 3 processes whose arrival time and burst time are given below-
| Process Id | Arrival time | Burst time |
| P1 | 0 | 2 |
| P2 | 3 | 1 |
| P3 | 5 | 6 |
If the CPU scheduling policy is FCFS, calculate the average waiting time and average turn around time.
Solution-
Gantt Chart-
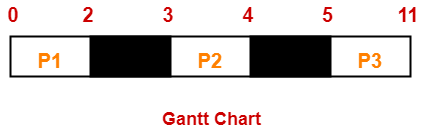
Here, black box represents the idle time of CPU.
Now, we know-
- Turn Around time = Exit time – Arrival time
- Waiting time = Turn Around time – Burst time
| Process Id | Exit time | Turn Around time | Waiting time |
| P1 | 2 | 2 – 0 = 2 | 2 – 2 = 0 |
| P2 | 4 | 4 – 3 = 1 | 1 – 1 = 0 |
| P3 | 11 | 11- 5 = 6 | 6 – 6 = 0 |
Now,
- Average Turn Around time = (2 + 1 + 6) / 3 = 9 / 3 = 3 unit
- Average waiting time = (0 + 0 + 0) / 3 = 0 / 3 = 0 unit
Problem-03:
Consider the set of 6 processes whose arrival time and burst time are given below-
| Process Id | Arrival time | Burst time |
| P1 | 0 | 3 |
| P2 | 1 | 2 |
| P3 | 2 | 1 |
| P4 | 3 | 4 |
| P5 | 4 | 5 |
| P6 | 5 | 2 |
If the CPU scheduling policy is FCFS and there is 1 unit of overhead in scheduling the processes, find the efficiency of the algorithm.
Solution-
Gantt Chart-
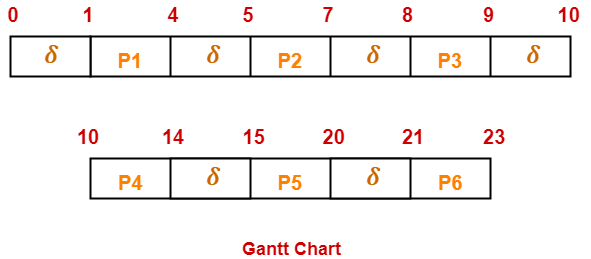
Here, δ denotes the context switching overhead.
Now,
- Useless time / Wasted time = 6 x δ = 6 x 1 = 6 unit
- Total time = 23 unit
- Useful time = 23 unit – 6 unit = 17 unit
Efficiency (η)
= Useful time / Total Total
= 17 unit / 23 unit
= 0.7391













No comments:
Post a Comment