If n pigeonholes are occupied by n+1 or more pigeons, then at least one pigeonhole is occupied by greater than one pigeon. Generalized pigeonhole principle is: - If n pigeonholes are occupied by kn+1 or more pigeons, where k is a positive integer, then at least one pigeonhole is occupied by k+1 or more pigeons.
Example1: Find the minimum number of students in a class to be sure that three of them are born in the same month.
Solution: Here n = 12 months are the Pigeonholes
And k + 1 = 3
K = 2
Example2: Show that at least two people must have their birthday in the same month if 13 people are assembled in a room.
Solution: We assigned each person the month of the year on which he was born. Since there are 12 months in a year.
So, according to the pigeonhole principle, there must be at least two people assigned to the same month.
Inclusion-Exclusion Principle:
Let A1,A2......Ar be the subset of Universal set U. Then the number m of the element which do not appear in any subset A1,A2......Ar of U.
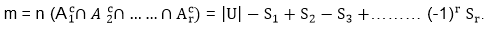
Example: Let U be the set of positive integer not exceeding 1000. Then |U|= 1000 Find |S| where S is the set of such integer which is not divisible by 3, 5 or 7?
Solution: Let A be the subset of integer which is divisible by 3
Let B be the subset of integer which is divisible by 5
Let C be the subset of integer which is divisible by 7
Then S = Ac ∩ Bc∩ Cc since each element of S is not divisible by 3, 5, or 7.
By Integer division,
|A|= 1000/3 = 333
|B|= 1000/5 = 200
|C| = 1000/7 = 142
|A∩B|=1000/15=66
|B∩C|=1000/21=47
|C∩A|=1000/35=28
|A∩B∩C|=1000/105=9
Thus by Inclusion-Exclusion Principle
|S|=1000-(333+200+142)+(66+47+28)-9
|S|=1000-675+141-9=457













No comments:
Post a Comment