Introduction of Input-Output Processor
The DMA mode of data transfer reduces CPU’s overhead in handling I/O operations. It also allows parallelism in CPU and I/O operations. Such parallelism is necessary to avoid wastage of valuable CPU time while handling I/O devices whose speeds are much slower as compared to CPU. The concept of DMA operation can be extended to relieve the CPU further from getting involved with the execution of I/O operations. This gives rises to the development of special purpose processor called Input-Output Processor (IOP) or IO channel.
The Input Output Processor (IOP) is just like a CPU that handles the details of I/O operations. It is more equipped with facilities than those are available in typical DMA controller. The IOP can fetch and execute its own instructions that are specifically designed to characterize I/O transfers. In addition to the I/O – related tasks, it can perform other processing tasks like arithmetic, logic, branching and code translation. The main memory unit takes the pivotal role. It communicates with processor by the means of DMA.
The block diagram –
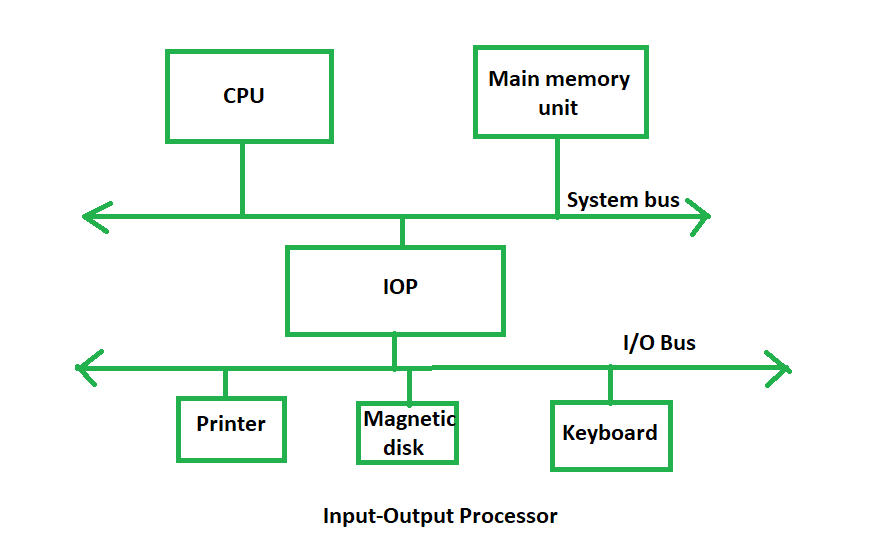
The Input Output Processor is a specialized processor which loads and stores data into memory along with the execution of I/O instructions. It acts as an interface between system and devices. It involves a sequence of events to executing I/O operations and then store the results into the memory.
Advantages –
- The I/O devices can directly access the main memory without the intervention by the processor in I/O processor based systems.
- It is used to address the problems that are arises in Direct memory access method.








No comments:
Post a Comment