DNS is a host name to IP address translation service. DNS is a distributed database implemented in a hierarchy of name servers. It is an application layer protocol for message exchange between clients and servers.
Requirement
Every host is identified by the IP address but remembering numbers is very difficult for the people and also the IP addresses are not static therefore a mapping is required to change the domain name to IP address. So DNS is used to convert the domain name of the websites to their numerical IP address.
- Generic domain : .com(commercial) .edu(educational) .mil(military) .org(non profit organization) .net(similar to commercial) all these are generic domain.
- Country domain .in (india) .us .uk
- Inverse domain if we want to know what is the domain name of the website. Ip to domain name mapping.So DNS can provide both the mapping for example to find the ip addresses of geeksforgeeks.org then we have to type nslookup www.geeksforgeeks.org.

Namespace – Set of possible names, flat or hierarchical . Naming system maintains a collection of bindings of names to values – given a name, a resolution mechanism returns the corresponding value –

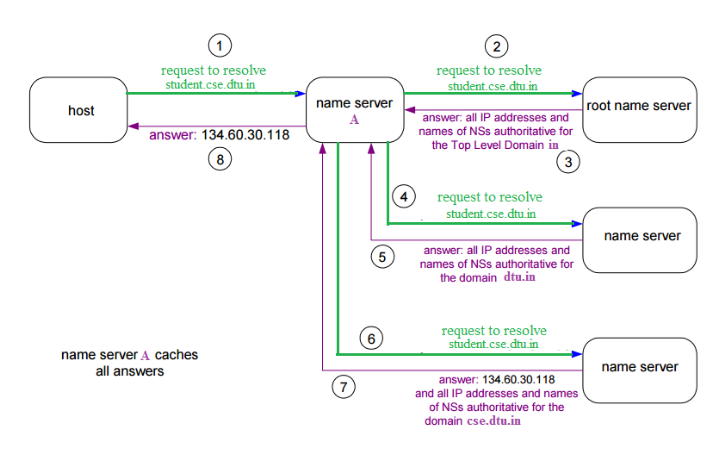
Top level server – It is responsible for com, org, edu etc and all top level country domains like uk, fr, ca, in etc. They have info about authoritative domain servers and know names and IP addresses of each authoritative name server for the second level domains.
Authoritative name servers This is organization’s DNS server, providing authoritative hostName to IP mapping for organization servers. It can be maintained by organization or service provider. In order to reach cse.dtu.in we have to ask the root DNS server, then it will point out to the top level domain server and then to authoritative domain name server which actually contains the IP address. So the authoritative domain server will return the associative ip address.
Domain Name Server













No comments:
Post a Comment