The World Wide Web abbreviated as WWW and commonly known as the web. The WWW was initiated by CERN (European library for Nuclear Research) in 1989.
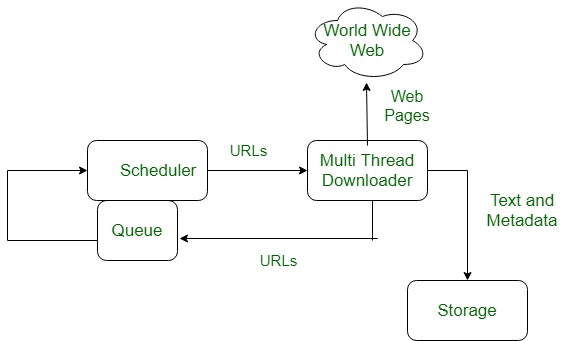
The basic model of how the web works is shown in figure below. Here the browser is displaying a web page on the client machine. When the user clicks on a line of text that is linked to a page on the abd.com server, the browser follows the hyperlink by sending a message to the abd.com server asking it for the page.
An Web browser is used to access webpages. Web browsers can be defined as programs which display text, data, pictures, animation and video on the Internet. Hyperlinked resources on the World Wide Web can be accessed using software interface provided by Web browsers. Initially Web browsers were used only for surfing the Web but now they have become more universal. Web browsers can be used for several tasks including conducting searches, mailing, transferring files, and much more. Some of the commonly used browsers are Internet Explorer, Opera Mini, Google Chrome.
Features of WWW:
- HyperText Information System
- Cross-Platform
- Distributed
- Open Standards and Open Source
- Uses Web Browsers to provide a single interface for many services
- Dynamic, Interactive and Evolving.
- “Web 2.0”
- Uniform Resource Locator (URL): serves as system for resources on web.
- HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP): specifies communication of browser and server.
- Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML): defines structure, organisation and content of webpage.







No comments:
Post a Comment