Storage Allocation
The different ways to allocate memory are:
- Static storage allocation
- Stack storage allocation
- Heap storage allocation
Static storage allocation
- In static allocation, names are bound to storage locations.
- If memory is created at compile time then the memory will be created in static area and only once.
- Static allocation supports the dynamic data structure that means memory is created only at compile time and deallocated after program completion.
- The drawback with static storage allocation is that the size and position of data objects should be known at compile time.
- Another drawback is restriction of the recursion procedure.
Stack Storage Allocation
- In static storage allocation, storage is organized as a stack.
- An activation record is pushed into the stack when activation begins and it is popped when the activation end.
- Activation record contains the locals so that they are bound to fresh storage in each activation record. The value of locals is deleted when the activation ends.
- It works on the basis of last-in-first-out (LIFO) and this allocation supports the recursion process.
Heap Storage Allocation
- Heap allocation is the most flexible allocation scheme.
- Allocation and deallocation of memory can be done at any time and at any place depending upon the user's requirement.
- Heap allocation is used to allocate memory to the variables dynamically and when the variables are no more used then claim it back.
- Heap storage allocation supports the recursion process.
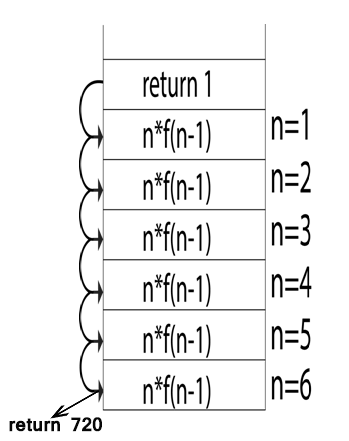
Example:
The dynamic allocation is as follows:





No comments:
Post a Comment