The word "Trie" is an excerpt from the word "retrieval". Trie is a sorted tree-based data-structure that stores the set of strings. It has the number of pointers equal to the number of characters of the alphabet in each node. It can search a word in the dictionary with the help of the word's prefix. For example, if we assume that all strings are formed from the letters 'a' to 'z' in the English alphabet, each trie node can have a maximum of 26 points.
Trie is also known as the digital tree or prefix tree. The position of a node in the Trie determines the key with which that node is connected.
Properties of the Trie for a set of the string:
- The root node of the trie always represents the null node.
- Each child of nodes is sorted alphabetically.
- Each node can have a maximum of 26 children (A to Z).
- Each node (except the root) can store one letter of the alphabet.
The diagram below depicts a trie representation for the bell, bear, bore, bat, ball, stop, stock, and stack.
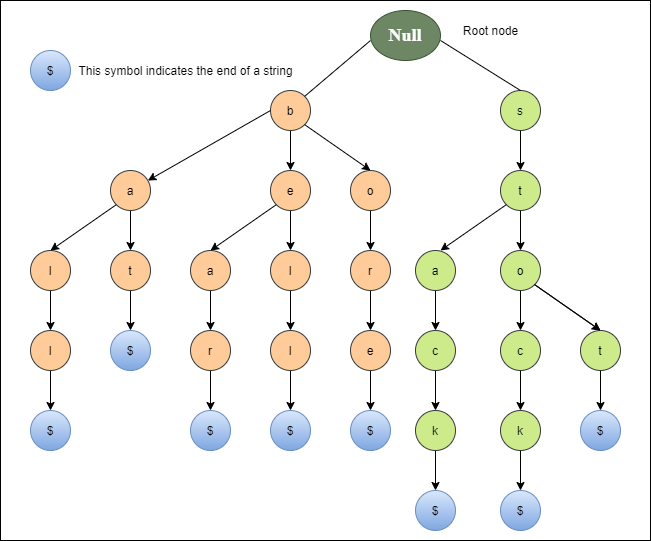
Basic operations of Trie
There are three operations in the Trie:
- Insertion of a node
- Searching a node
- Deletion of a node
Insert of a node in the Trie
The first operation is to insert a new node into the trie. Before we start the implementation, it is important to understand some points:
- Every letter of the input key (word) is inserted as an individual in the Trie_node. Note that children point to the next level of Trie nodes.
- The key character array acts as an index of children.
- If the present node already has a reference to the present letter, set the present node to that referenced node. Otherwise, create a new node, set the letter to be equal to the present letter, and even start the present node with this new node.
- The character length determines the depth of the trie.
Searching a node in Trie
The second operation is to search for a node in a Trie. The searching operation is similar to the insertion operation. The search operation is used to search a key in the trie.
Deletion of a node in the Trie
The Third operation is the deletion of a node in the Trie. Before we begin the implementation, it is important to understand some points:
- If the key is not found in the trie, the delete operation will stop and exit it.
- If the key is found in the trie, delete it from the trie.
Applications of Trie
1. Spell Checker
Spell checking is a three-step process. First, look for that word in a dictionary, generate possible suggestions, and then sort the suggestion words with the desired word at the top.
Trie is used to store the word in dictionaries. The spell checker can easily be applied in the most efficient way by searching for words on a data structure. Using trie not only makes it easy to see the word in the dictionary, but it is also simple to build an algorithm to include a collection of relevant words or suggestions.
2. Auto-complete
Auto-complete functionality is widely used on text editors, mobile applications, and the Internet. It provides a simple way to find an alternative word to complete the word for the following reasons.
- It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.
- We trace pointers only to get the node that represents the string entered by the user.
- As soon as you start typing, it tries to complete your input.
3. Browser history
It is also used to complete the URL in the browser. The browser keeps a history of the URLs of the websites you've visited.
Advantages of Trie
- It can be insert faster and search the string than hash tables and binary search trees.
- It provides an alphabetical filter of entries by the key of the node.
Disadvantages of Trie
- It requires more memory to store the strings.
- It is slower than the hash table.













No comments:
Post a Comment