Decision Tree Classification Algorithm
- Decision Tree is a Supervised learning technique that can be used for both classification and Regression problems, but mostly it is preferred for solving Classification problems. It is a tree-structured classifier, where internal nodes represent the features of a dataset, branches represent the decision rules and each leaf node represents the outcome.
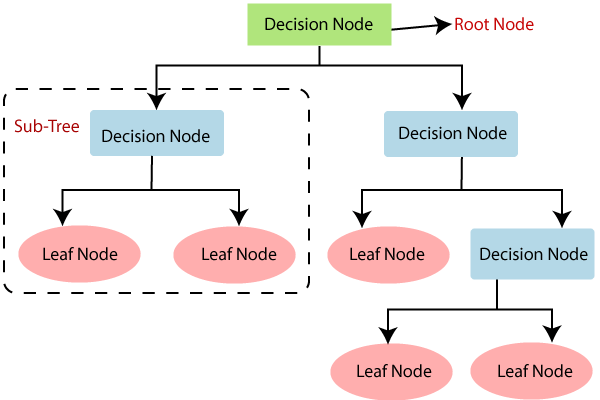
- In a Decision tree, there are two nodes, which are the Decision Node and Leaf Node. Decision nodes are used to make any decision and have multiple branches, whereas Leaf nodes are the output of those decisions and do not contain any further branches.
- The decisions or the test are performed on the basis of features of the given dataset.
- It is a graphical representation for getting all the possible solutions to a problem/decision based on given conditions.
- It is called a decision tree because, similar to a tree, it starts with the root node, which expands on further branches and constructs a tree-like structure.
- In order to build a tree, we use the CART algorithm, which stands for Classification and Regression Tree algorithm.
- A decision tree simply asks a question, and based on the answer (Yes/No), it further split the tree into subtrees.
- Below diagram explains the general structure of a decision tree:
Note: A decision tree can contain categorical data (YES/NO) as well as numeric data.
Why use Decision Trees?
There are various algorithms in Machine learning, so choosing the best algorithm for the given dataset and problem is the main point to remember while creating a machine learning model. Below are the two reasons for using the Decision tree:
- Decision Trees usually mimic human thinking ability while making a decision, so it is easy to understand.
- The logic behind the decision tree can be easily understood because it shows a tree-like structure.
Decision Tree Terminologies
How does the Decision Tree algorithm Work?
In a decision tree, for predicting the class of the given dataset, the algorithm starts from the root node of the tree. This algorithm compares the values of root attribute with the record (real dataset) attribute and, based on the comparison, follows the branch and jumps to the next node.
For the next node, the algorithm again compares the attribute value with the other sub-nodes and move further. It continues the process until it reaches the leaf node of the tree. The complete process can be better understood using the below algorithm:
- Step-1: Begin the tree with the root node, says S, which contains the complete dataset.
- Step-2: Find the best attribute in the dataset using Attribute Selection Measure (ASM).
- Step-3: Divide the S into subsets that contains possible values for the best attributes.
- Step-4: Generate the decision tree node, which contains the best attribute.
- Step-5: Recursively make new decision trees using the subsets of the dataset created in step -3. Continue this process until a stage is reached where you cannot further classify the nodes and called the final node as a leaf node.
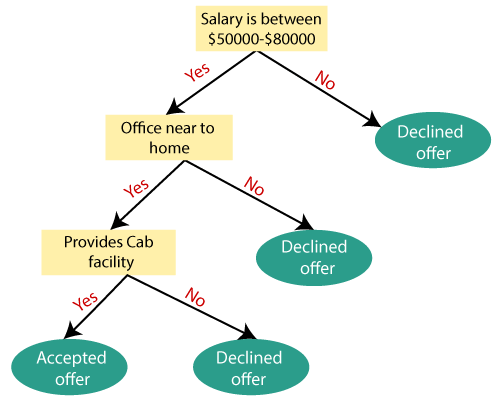
Example: Suppose there is a candidate who has a job offer and wants to decide whether he should accept the offer or Not. So, to solve this problem, the decision tree starts with the root node (Salary attribute by ASM). The root node splits further into the next decision node (distance from the office) and one leaf node based on the corresponding labels. The next decision node further gets split into one decision node (Cab facility) and one leaf node. Finally, the decision node splits into two leaf nodes (Accepted offers and Declined offer). Consider the below diagram:




No comments:
Post a Comment