Support Vector Machine Algorithm
Support Vector Machine or SVM is one of the most popular Supervised Learning algorithms, which is used for Classification as well as Regression problems. However, primarily, it is used for Classification problems in Machine Learning.
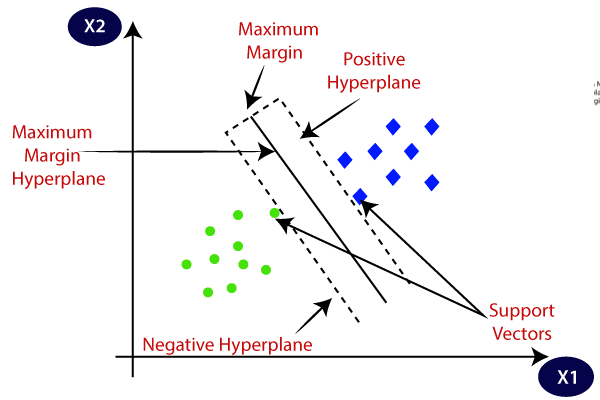
The goal of the SVM algorithm is to create the best line or decision boundary that can segregate n-dimensional space into classes so that we can easily put the new data point in the correct category in the future. This best decision boundary is called a hyperplane.
SVM chooses the extreme points/vectors that help in creating the hyperplane. These extreme cases are called as support vectors, and hence algorithm is termed as Support Vector Machine. Consider the below diagram in which there are two different categories that are classified using a decision boundary or hyperplane:
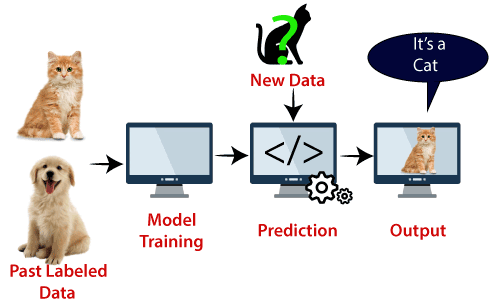
Example: SVM can be understood with the example that we have used in the KNN classifier. Suppose we see a strange cat that also has some features of dogs, so if we want a model that can accurately identify whether it is a cat or dog, so such a model can be created by using the SVM algorithm. We will first train our model with lots of images of cats and dogs so that it can learn about different features of cats and dogs, and then we test it with this strange creature. So as support vector creates a decision boundary between these two data (cat and dog) and choose extreme cases (support vectors), it will see the extreme case of cat and dog. On the basis of the support vectors, it will classify it as a cat. Consider the below diagram:
SVM algorithm can be used for Face detection, image classification, text categorization, etc.




No comments:
Post a Comment