Calculate the address of any element in the 3-D Array:
A 3-Dimensional array is a collection of 2-Dimensional arrays. It is specified by using three subscripts:
- Block size
- Row size
- Column size
More dimensions in an array mean more data can be stored in that array.
Example:
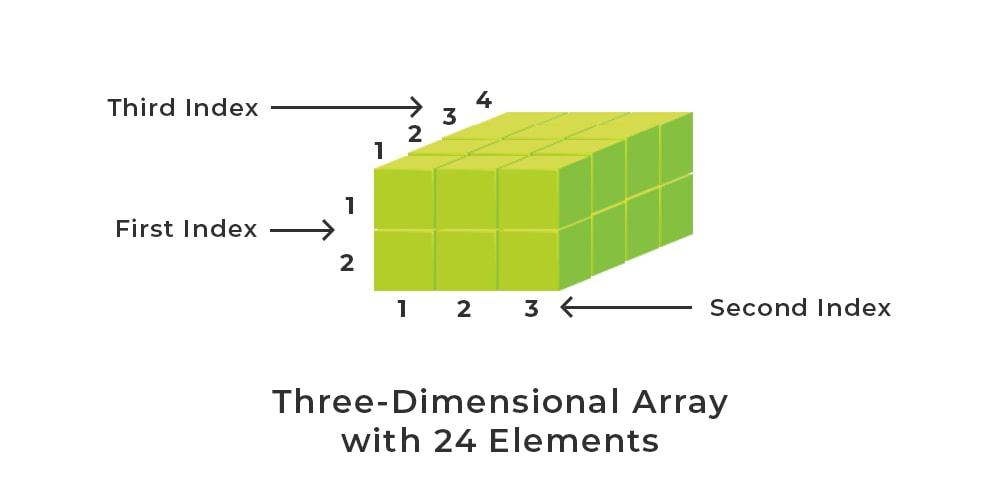
3-D array
To find the address of any element in 3-Dimensional arrays there are the following two ways-
- Row Major Order
- Column Major Order
1. Row Major Order:
To find the address of the element using row-major order, use the following formula:
Address of A[i][j][k] = B + W (M * N(i-x) + N *(j-y) + (k-z))
Here:
B = Base Address (start address)W = Weight (storage size of one element stored in the array)M = Row (total number of rows)N = Column (total number of columns)P = Width (total number of cells depth-wise)x = Lower Bound of Rowy = Lower Bound of Columnz = Lower Bound of Width
Example: Given an array, arr[1:9, -4:1, 5:10] with a base value of 400 and the size of each element is 2 Bytes in memory find the address of element arr[5][-1][8] with the help of row-major order?
Solution:
Given:Row Subset of an element whose address to be found I = 5Column Subset of an element whose address to be found J = -1Block Subset of an element whose address to be found K = 8Base address B = 400Storage size of one element store in any array(in Byte) W = 2Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix x = 1Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix y = -4Lower Limit of blocks in matrix z = 5M = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1 = 1 – (-4) + 1 = 6N = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1 = 10 – 5 + 1 = 6Formula used:Address of[I][J][K] =B + W (M * N(i-x) + N *(j-y) + (k-z))Solution:Address of[][][] = 400 + 2 * {[6 * 6 * (5 – 1)] + 6 * [(-1 + 4)]} + [8 – 5]= 400 + 2 * ((4 * 6 + 3) * 6 + 3)= 400 + 2 * (165)= 730
2. Column Major Order:
To find the address of the element using column-major order, use the following formula:1
Address of A[i][j][k = B + W(M * N(i – x) + M *(k – z) + (j – y))
Here:
B = Base Address (start address)W = Weight (storage size of one element stored in the array)M = Row (total number of rows)N = Column (total number of columns)P = Width (total number of cells depth-wise)x = Lower Bound of Rowy = Lower Bound of Columnz = Lower Bound of Width
Example: Given an array arr[1:8, -5:5, -10:5] with a base value of 400 and the size of each element is 4 Bytes in memory find the address of element arr[3][3][3] with the help of column-major order?
Solution:
Given:Row Subset of an element whose address to be found I = 3Column Subset of an element whose address to be found J = 3Block Subset of an element whose address to be found K = 3Base address B = 400Storage size of one element store in any array(in Byte) W = 4Lower Limit of row/start row index of matrix x = 1Lower Limit of column/start column index of matrix y = -5Lower Limit of blocks in matrix z = -10M = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1 = 5 + 5 + 1 = 11N = Upper Bound – Lower Bound + 1 = 5 + 10 + 1 = 16Formula used:Address of[i][j][k] = B + W(M * N(i – x) + M * (k – z) + (j – y))Solution:Address of[3][3][3] = 400 + 4 * {[(3 – 1)] * 16 + [3 + 10] ]} * 11 + [3 + 5]= 400 + 4 * ((32 + 13) * 11 + 8)= 400 + 4 * (503)= 400 + 2012= 2412
N-Dimensional Arrays:
The N-Dimensional array is basically an array of arrays. As 1-D arrays are identified as a single index, 2-D arrays are identified using two indices, similarly, N-Dimensional arrays are identified using N indices. A multi-dimensional array is declared as follows:
int NDA[S1][S2][S3]……..[SN];
Explanation:
- Here, NDA is the name of the N-Dimensional array. It can be any valid identifier name.
- In the above syntax, S1, S2, S3……SN denotes the max sizes of the N dimensions.
- The lower bounds are assumed to be zeroes for all the dimensions.
- The above array is declared as an integer array. It can be any valid data type other than an integer as well.
Address Calculation of N-Dimensional Arrays:
Assumptions:
- The N-Dimensional array NDA with the maximum sizes of N dimensions are S1, S2, S3, ………, SN.
- The element whose address needs to be calculated has indices l1, l2, l3, …………..lN respectively.
- It is possible that the array indices do not have the lower bound as zero. For example, consider the following array T: T[-5…5][2……9][14…54][-9…-2].
Explanation:
- In the above array T, the lower bounds of indices are not zeroes.
- So that the sizes of the indices of the array are different now and can be calculated by using the formula:
UpperBound – LowerBound +1
- So, here the S1 = 5 – (-5) + 1 = 11. Similarly, S2 = 8, S3 = 41 and S4 = 8.
For address calculation, the lower bounds are t1, t2, t3…….tN. There exist two ways to store the array elements:
- Row Major
- Column Major
The Column Major formula:
Address of NDA[I1][I2]. . . [IN] = BAd + W*[((…ENSN-1+ EN-1 )SN-2 +… E3 )S2+ E2 )S1 +E1]
- BAd represents the base address of the array.
- W is Storage Size of one element stored in the array (in byte).
- Also, Ei is given by Ei = li – ti, where li and ti are the calculated indexes (indices of array element which needs to be determined) and lower bounds respectively.
The Row Major formula:
Address of NDA[I1][I2]. . . .[lN] = BAd + W*[((E1S2 + E2 )S3 +E3 )S4 ….. + EN-1 )SN + EN]
The simplest way to learn the formulas:
For row-major: If width = 5, the interior sequence is E1S2 + E2S3 + E3S4 + E4S5 + E5 and if width = 3, the interior sequence is E1S2 + E2S3 + E3. Figure out the pattern in the order and follow four basic steps for the formula of any width:
- Write the interior sequence.
- Put the closing bracket after each E except the first term. So for width = 5, it becomes
E1S2 + E2)S3 + E3)S4 + E4)S5 + E5).
- Put all the Opening brackets initially.
((((E1S2 + E2)S3 + E3)S4 + E4)S5 + E5).
- Incorporate the base address and width in the formula.
The approach is similar for the Column Major but the pattern of the interior sequence is reverse of the row-major pattern.
For column-major: If width =5, the interior sequence is E5S4 + E4S3 + E3S2+ E2S1 + E1.
Example: Let’s take a multi-dimensional array A[10][20][30][40] with the base address 1200. The task is to find the address of element A[1][3][5][6].
A[1][3][5][6] = 1200 + 4(((1 × 20 + 3)30 +5)40 + 6)
=1200 +4((23 × 30 +5)40 +6)
=1200 + 4(695 × 40 + 6)
=1200 + (4 × 27806)
=112424.
Example: Suppose multidimensional array A and B are declared using A [-2:2, 2:22] and B [1:8, -5:5, -10:5].
AKTU 2018-19, Marks 07
Solution:- The dimensions of A are :
M=8 , N=5, R=7, i=5, j=3, k=6
Rows - wise :
Location (A[i,j,k]) = BA + MN(k-1) + N(i-1) + (j-1)
Location(A[5,3,6])= 900 + 8x5(6-1) + 5(5-1) + (3-1)
= 900 + 40 x 5 +5 x 4 + 2
= 900 + 200 +20 +2
= 1122
Columns - wise :
Location (A[i,j,k]) = BA + MN(k-1) + M(j-1) + (i-1)
Location (A[5,3,6]) = 900 + 8x5(6-1) + 8(3-1) + (5-1)
= 900 + 40 x 5 +8 x 2 + 4
= 900 + 200 +16 +4
= 1120





No comments:
Post a Comment