Event and Listener (Java Event Handling)
| Changing the state of an object is known as an event. For example, click on button, dragging mouse etc. The java.awt.event package provides many event classes and Listener interfaces for event handling. |
Java Event classes and Listener interfaces
|
Event Classes |
Listener Interfaces |
|
ActionEvent |
ActionListener |
|
MouseEvent |
MouseListener and
MouseMotionListener |
|
MouseWheelEvent |
MouseWheelListener |
|
KeyEvent |
KeyListener |
|
ItemEvent |
ItemListener |
|
TextEvent |
TextListener |
|
AdjustmentEvent |
AdjustmentListener |
|
WindowEvent |
WindowListener |
|
ComponentEvent |
ComponentListener |
|
ContainerEvent |
ContainerListener |
|
FocusEvent |
FocusListener |
Steps to perform Event Handling
Following steps are required to perform event handling:
- Register the component with the Listener
Registration Methods
For registering the component with the Listener, many classes provide the registration methods. For example:
- Button
- public void addActionListener(ActionListener a){}
- MenuItem
- public void addActionListener(ActionListener a){}
- TextField
- public void addActionListener(ActionListener a){}
- public void addTextListener(TextListener a){}
- TextArea
- public void addTextListener(TextListener a){}
- Checkbox
- public void addItemListener(ItemListener a){}
- Choice
- public void addItemListener(ItemListener a){}
- List
- public void addActionListener(ActionListener a){}
- public void addItemListener(ItemListener a){}
Java Event Handling Code
We can put the event handling code into one of the following places:
- Within class
- Other class
- Anonymous class
Java event handling by implementing ActionListener
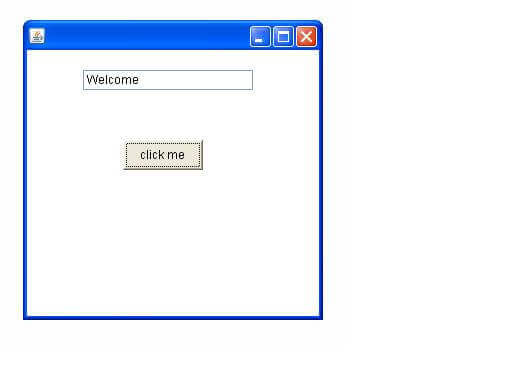
import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;class AEvent extends Frame implements ActionListener{TextField tf;AEvent(){//create componentstf=new TextField();tf.setBounds(60,50,170,20);Button b=new Button("click me");b.setBounds(100,120,80,30);//register listenerb.addActionListener(this);//passing current instance//add components and set size, layout and visibilityadd(b);add(tf);setSize(300,300);setLayout(null);setVisible(true);}public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){tf.setText("Welcome");}public static void main(String args[]){new AEvent();}}
public void setBounds(int xaxis, int yaxis, int width, int height); have been used in the above example that sets the position of the component it may be button, textfield etc.
2) Java event handling by outer class
import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;class AEvent2 extends Frame{TextField tf;AEvent2(){//create componentstf=new TextField();tf.setBounds(60,50,170,20);Button b=new Button("click me");b.setBounds(100,120,80,30);//register listenerOuter o=new Outer(this);b.addActionListener(o);//passing outer class instance//add components and set size, layout and visibilityadd(b);add(tf);setSize(300,300);setLayout(null);setVisible(true);}public static void main(String args[]){new AEvent2();}}
import java.awt.event.*;
class Outer implements ActionListener{
AEvent2 obj;
Outer(AEvent2 obj){
this.obj=obj;
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){
obj.tf.setText("welcome");
}
}
3) Java event handling by anonymous class
import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;class AEvent3 extends Frame{TextField tf;AEvent3(){tf=new TextField();tf.setBounds(60,50,170,20);Button b=new Button("click me");b.setBounds(50,120,80,30);b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){public void actionPerformed(){tf.setText("hello");}});add(b);add(tf);setSize(300,300);setLayout(null);setVisible(true);}public static void main(String args[]){new AEvent3();}}




No comments:
Post a Comment