Auxiliary Memory
An Auxiliary memory is known as the lowest-cost, highest-capacity and slowest-access storage in a computer system. It is where programs and data are kept for long-term storage or when not in immediate use. The most common examples of auxiliary memories are magnetic tapes and magnetic disks.
Magnetic Disks
A magnetic disk is a type of memory constructed using a circular plate of metal or plastic coated with magnetized materials. Usually, both sides of the disks are used to carry out read/write operations. However, several disks may be stacked on one spindle with read/write head available on each surface.
The following image shows the structural representation for a magnetic disk.
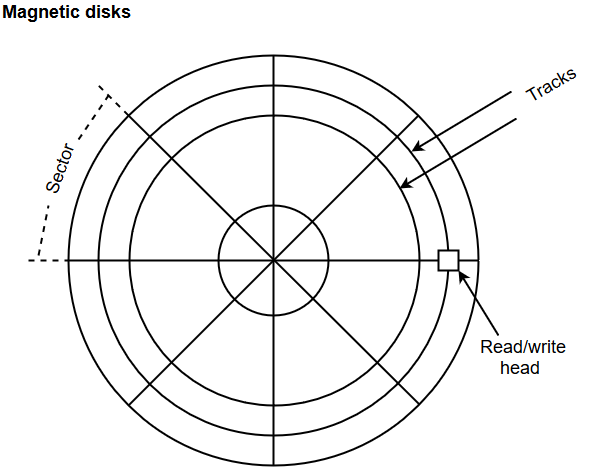
- The memory bits are stored in the magnetized surface in spots along the concentric circles called tracks.
- The concentric circles (tracks) are commonly divided into sections called sectors.
Magnetic Tape
Magnetic tape is a storage medium that allows data archiving, collection, and backup for different kinds of data. The magnetic tape is constructed using a plastic strip coated with a magnetic recording medium.
The bits are recorded as magnetic spots on the tape along several tracks. Usually, seven or nine bits are recorded simultaneously to form a character together with a parity bit.
Magnetic tape units can be halted, started to move forward or in reverse, or can be rewound. However, they cannot be started or stopped fast enough between individual characters. For this reason, information is recorded in blocks referred to as records.
Optical Disc?
An optical disc is an electronic data storage medium that is also referred to as an optical disk, optical storage, optical media, Optical disc drive, disc drive, which reads and writes data by using optical storage techniques and technology. An optical disc, which may be used as a portable and secondary storage device, was first developed in the late 1960s. James T. Russell invented the first optical disc, which could store data as micron-sized light and dark dots.

An optical disc can store more data and has a longer lifespan than the preceding generation of magnetic storage medium. To read and write to CDs and DVDs, computers use a CD writer or DVD writer drive, and to read and write to Blu-ray discs, they require a Blu-ray drive. MO drives, such as CD-R and DVD-R drives, are used to read and write information to discs (magneto-optic). The CDs, Blu-ray, and DVDs are the most common types of optical media, which are usually used to:
- They are used to transfer data to various devices or computers.
- These media are used to deliver the software to others.
- They help users to hold large amounts of data, like videos, photos, music, and more.
- Also, optical media are used to get back up from a local machine.
With the introduction of an all-new generation of optical media, the storage capacity to store data has increased. CDs have the potential to store 700 MB of data, whereas DVDs allow you to store up to 8.4 GB of data. Blu-ray discs, the newest type of optical media, can hold up to 50 GB of data. This storage capacity is the most convenient benefit as compared to the floppy disk storage media, which can store up to 1.44 MB of data.
Optical discs are impervious to most environmental threats like magnetic disturbances or power surges; however, these discs are not expensive to manufacture. It helps optical disc storage to make well-suited for archival storage. Sony said in 2016 that it would release a Blu-ray disc with the capacity to hold 3.3 terabytes (TB) of data.
There is a need to be noted, a CD drive can only have the ability to read CDs, and a DVD drive can read CDs and DVDs. Additionally, a Blu-ray, a new type of optical media that can read CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs. In other words, older drives are not able to read newer optical discs, but the latest drives have the ability to read older optical discs.
How optical storage discs are made
The basic sandwich of materials structure is used by all recent optical disc formats. The base is formed by using a hard-plastic substrate, and a reflective layer of metallic foil is used for encoding the digital data. Next, a clear polycarbonate layer secures the foil and enables the laser beam to move via the reflective foil layer.
Optical discs include different materials in the sandwich, which are dependent on the type of disc, whether it is rewritable or write-once. In write-once CD-ROM, an organic dye layer is located between the polycarbonate and unwritten reflective foil. Because they replace the aluminium foil with an alloy that is a phase-change material, rewritable optical discs may be erased and rewritten several times.
What optical disc can hold the most?
Blu-ray discs, which are the newest type of optical media, have the potential to store the most, up to 50 GB of data. BD-R (Blu-ray recordable) is available in the market with a storage capacity of 25 GB or 50 GB.
Different Kinds of Optical Drives
Optical drives are disk-based drives that were introduced to the market in the 1980s to allow for increased storage capacity and faster read and write times. There are multiple kinds of optical media, which are discussed below:
CD-ROM
CD-ROM, short for compact disk read-only memory, was the first disk on the basis of drives for the latest PCs. CD-ROM devices populate Compact Disk Filing System discs with data encoded in ISO 9660. To reduce noise and increase stability, most CD-ROM drives in computers run at a slower speed, and if the drive experiences read errors, it will only speed up for larger data files. However, the newest CD-ROM drives have the potential to achieve read speeds of 60 revolutions in a second (60x).
DVD-ROM
DVD-ROM drives, which stand for Digital Versatile Disk Read Only Memory and are a direct evolution from CD-ROM drives, have significantly more performance and capacity than their CD counterparts while maintaining the same physical dimensions. The DVD Forum is a non-profit organization that establishes several standards for DVD functionality and construction, as well as overseeing DVD development.
Blu-ray
In the commercial market, Blu-ray drives are the newest drives available as of 2011. During the early 2000s, Sony developed the Blu-ray technology that was one of the founding proponents
RW Drives
The rewritable drive types are Blu-ray drives, DVD-ROMs, and CD-ROMs. All the functionalities of read-only counterparts are available in RW drives. Write processes are particularly sensitive to shock and can ruin the disc beyond repair if forcibly interrupted; write speeds are slower to preserve stability than read speeds. Writable disks come in multiple-time write and one-time write variations; however, RW drives can write multiple times.
Advantages of Optical Disk
There are various benefits of the optical disk, which are as follows:
Cost
Only plastics and aluminum foils are used in the production of an optical disk, which makes their manufacturing cost less expensive. Therefore, users get the advantage to purchase optical disks in bulk, and also, the optical disk drive is included with many computers by their manufacturers, and users can be benefited from purchasing optical disk drives separately.
Durability
While comparing with Volatile and Non-Volatile memories, optical disks are more durable. It is not caused to data losses due to any power failure and is not subjected to wear. Hence, it can run a long time. However, it is not much safe from any physical damages, including against scratching and heat.
Simplicity
With the help of using optical disks, the process of backup of data is much easier. The data should be placed inside the drive icon; the data, which needs to be burnt. And, the users can backup data easily only by clicking on "Burn Disk."
Stability
A very high level of stability is provided by optical disk because it is not unprotected from electromagnetic fields and other kinds of environmental influences, unlike magnetic disks.
Portability
Optical disks are very portable; however, they are fairly large in size. They can be used in different computers and devices and transported to different places as they can be placed inside bags and other small objects.
Disadvantages of Optical Disk
Although it has numerous advantages, it also contains some limitations that are discussed below:
Security
Optical disks need to keep safe from the hands of thieves when you are using them for backup purposes. If thieves get success in stealing optical disks, it can be more harmful. Hence, it may provide insecurity; and due to its size, there are more chances to optical disk more prone to lose and theft.
Reliability
Unlike flash drives, any plastic casings can be caused to damage optical disks. Therefore, they make the disk unreadable as they are prone to scratching the disks. The data stored on an optical disk cannot be recovered anymore.
Capacity
As compared to other forms of storage drives, the cost of optical disks is high per GB/TB. Also, while comparing with any other forms of storage medias, it has less storage capacity. Except the Blu-ray disk, the maximum storage capacity of optical disk is 4.7GB.
Duplication
Like a USB flash drive, it is not easy to make a duplicate copy by using an optical disk. There is needed a separate software and hardware in order to process of burning. For this purpose, also, there are multiple third-party programs available. Writing software is furnished with the newest version of windows.
User Friendliness
Actually, it is not appropriate in terms of backup; however, its manufacturing cost is very low. Some significant amounts are needed for Networks and Online backups for services. Furthermore, if an optical drive is under heavy use, it requires a replacement frequently, and it is known to possess high failure rates.
Why is optical media not as popular today?
The popularity of all-optical media has greatly decreased as almost all kinds of content are available on the internet, which can be downloaded and streamed anywhere with a network connection. Another reason optical media is not more common in use today, the price of USB flash drives has decreased, which has the potential to store a lot more data, which led to make optical media a less popular storage solution.













No comments:
Post a Comment