- Process Control Block (PCB) is a data structure that stores information about a particular process.
- This information is required by the CPU while executing the process.
The Process Control Block of a process looks like-
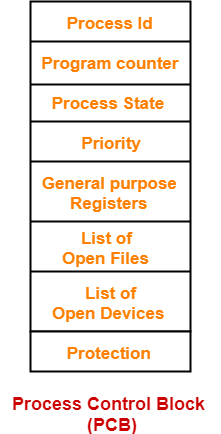
- Each process is identified by its own process control block (PCB).
- It is also called as context of the process.
Process Attributes-
The various attributes of process stored in the PCB are-
1. Process Id-
- Process Id is a unique Id that identifies each process of the system uniquely.
- A process Id is assigned to each process during its creation.
2. Program Counter-
- Program counter specifies the address of the instruction to be executed next.
- Before execution, program counter is initialized with the address of the first instruction of the program.
- After executing an instruction, value of program counter is automatically incremented to point to the next instruction.
- This process repeats till the end of the program.
3. Process State-
- Each process goes through different states during its lifetime.
- Process state specifies the current state of the process.
4. Priority-
- Priority specifies how urgent is to execute the process.
- Process with the highest priority is allocated the CPU first among all the processes.
5. General Purpose Registers-
- General purpose registers are used to hold the data of process generated during its execution.
- Each process has its own set of registers which are maintained by its PCB.
6. List of Open Files-
- Each process requires some files which must be present in the main memory during its execution.
- PCB maintains a list of files used by the process during its execution.
7. List of Open Devices-
- PCB maintains a list of open devices used by the process during its execution.
Important Notes-
- PCB of each process resides in the main memory.
- There exists only one PCB corresponding to each process.
- PCB of all the processes are present in a linked list.






No comments:
Post a Comment