It is moving of an object about an angle. Movement can be anticlockwise or clockwise. 3D rotation is complex as compared to the 2D rotation. For 2D we describe the angle of rotation, but for a 3D angle of rotation and axis of rotation are required. The axis can be either x or y or z.
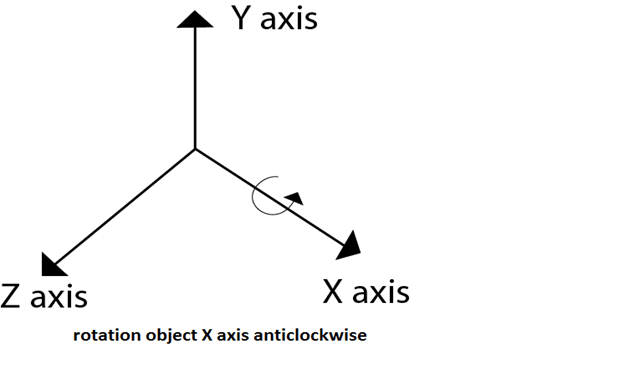
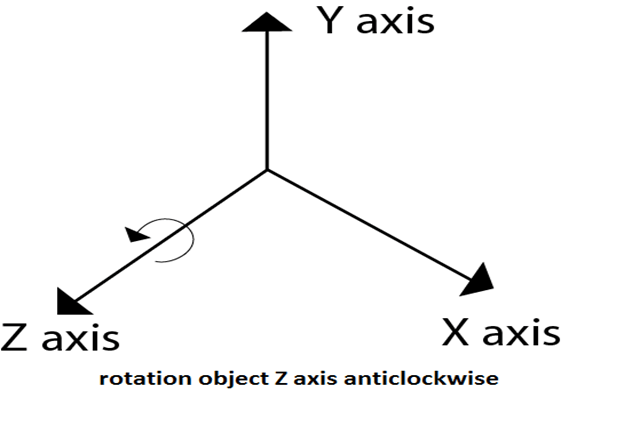
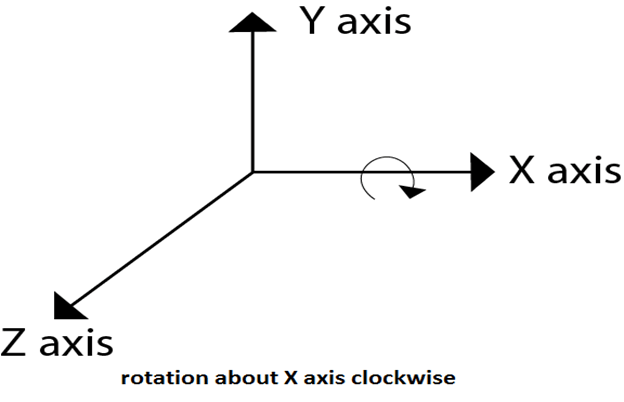
Following figures shows rotation about x, y, z- axis
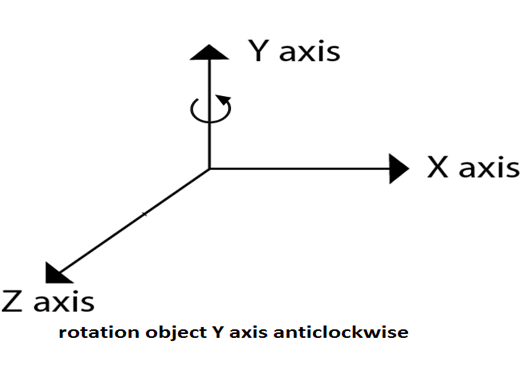
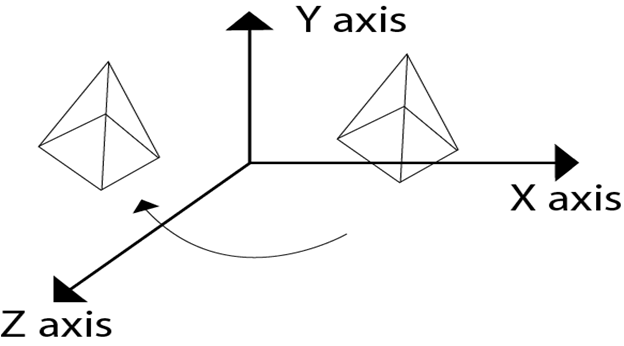
Following figure show rotation of the object about the Y axis
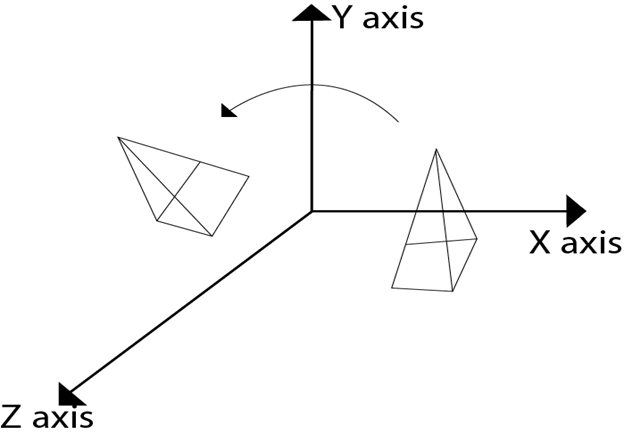
Following figure show rotation of the object about the Z axis
Rotation about Arbitrary Axis
When the object is rotated about an axis that is not parallel to any one of co-ordinate axis, i.e., x, y, z. Then additional transformations are required. First of all, alignment is needed, and then the object is being back to the original position. Following steps are required
- Translate the object to the origin
- Rotate object so that axis of object coincide with any of coordinate axis.
- Perform rotation about co-ordinate axis with whom coinciding is done.
- Apply inverse rotation to bring rotation back to the original position.
Matrix for representing three-dimensional rotations about the Z axis
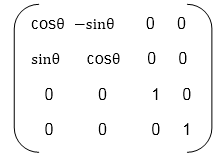
Matrix for representing three-dimensional rotations about the X axis
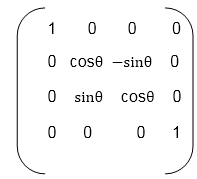
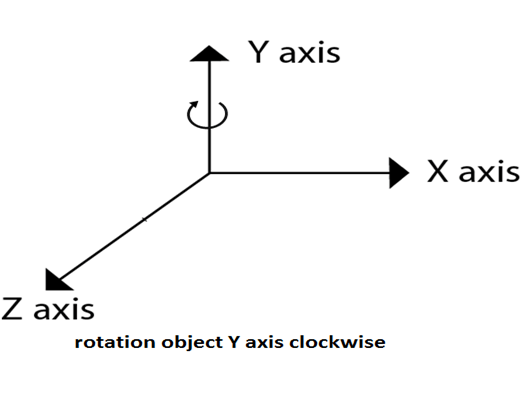
Matrix for representing three-dimensional rotations about the Y axis
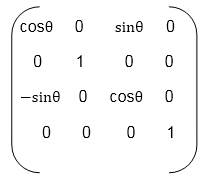
Following figure show the original position of object and position of object after rotation about the x-axis
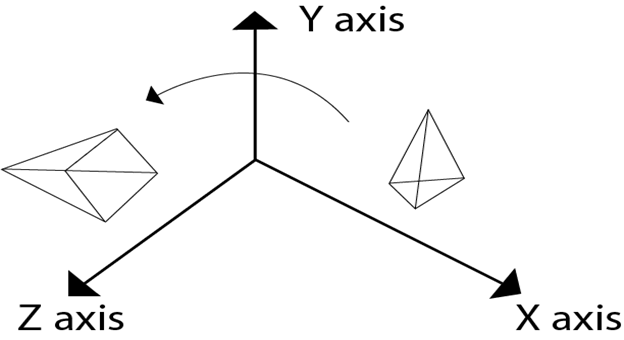
5. Apply inverse translation to bring rotation axis to the original position.
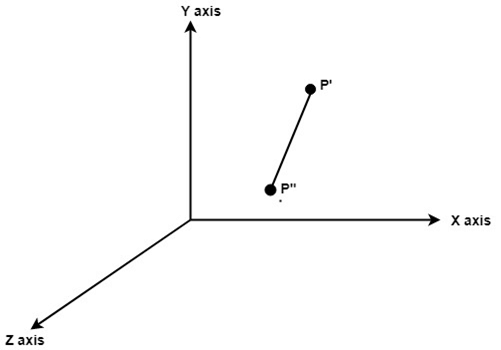
For such transformations, composite transformations are required. All the above steps are applied on points P' and P".Each step is explained using a separate figure.
Step1: Initial position of P' and P"is shown
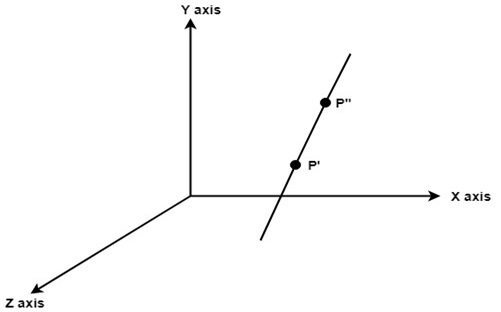
Step2: Translate object P' to origin
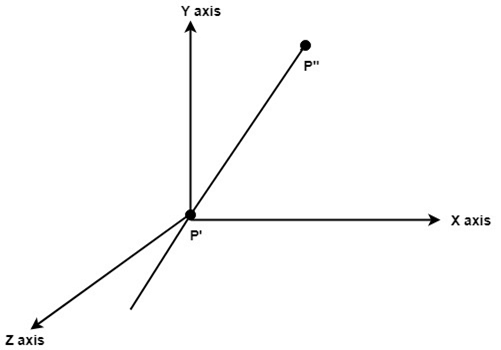
Step3: Rotate P" to z axis so that it aligns along the z-axis
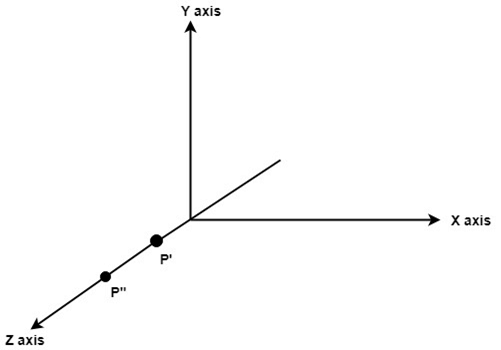
Step4: Rotate about around z- axis
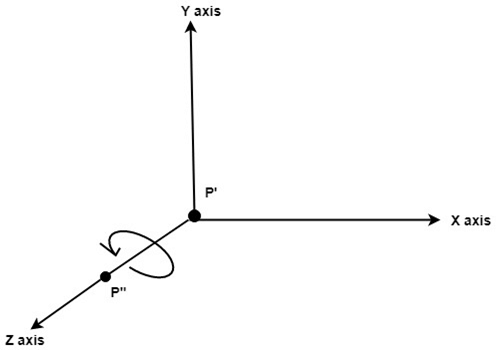
Step5: Rotate axis to the original position
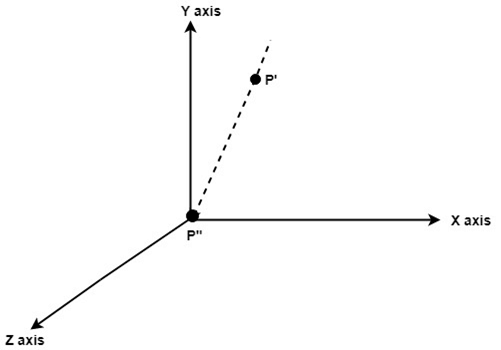
Step6: Translate axis to the original position.









No comments:
Post a Comment