Mapping Constraints
- A mapping constraint is a data constraint that expresses the number of entities to which another entity can be related via a relationship set.
- It is most useful in describing the relationship sets that involve more than two entity sets.
- For binary relationship set R on an entity set A and B, there are four possible mapping cardinalities. These are as follows:
- One to one (1:1)
- One to many (1:M)
- Many to one (M:1)
- Many to many (M:M)
- One to one (1:1)
- One to many (1:M)
- Many to one (M:1)
- Many to many (M:M)
One-to-one
In one-to-one mapping, an entity in E1 is associated with at most one entity in E2, and an entity in E2 is associated with at most one entity in E1.
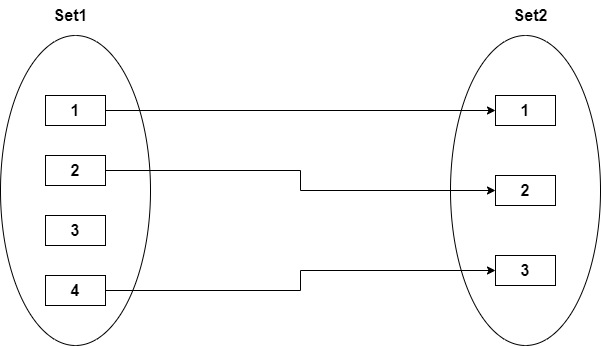
One-to-many
In one-to-many mapping, an entity in E1 is associated with any number of entities in E2, and an entity in E2 is associated with at most one entity in E1.
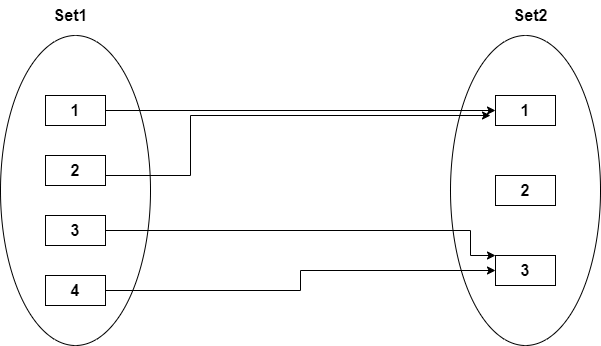
Many-to-one
In one-to-many mapping, an entity in E1 is associated with at most one entity in E2, and an entity in E2 is associated with any number of entities in E1.
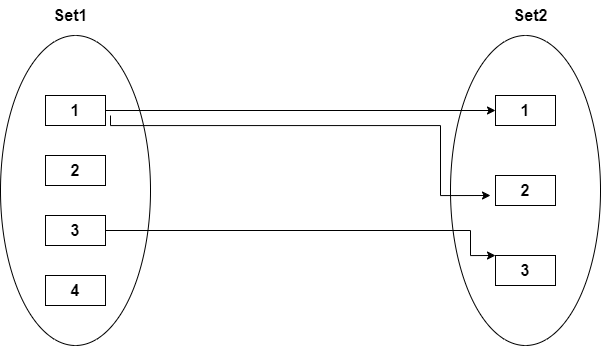
Many-to-many
In many-to-many mapping, an entity in E1 is associated with any number of entities in E2, and an entity in E2 is associated with any number of entities in E1.
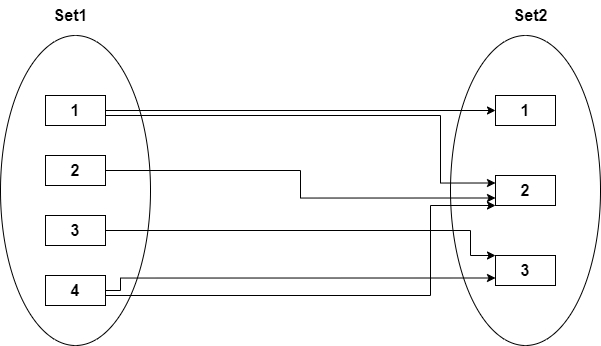
- A mapping constraint is a data constraint that expresses the number of entities to which another entity can be related via a relationship set.
- It is most useful in describing the relationship sets that involve more than two entity sets.
- For binary relationship set R on an entity set A and B, there are four possible mapping cardinalities. These are as follows:
- One to one (1:1)
- One to many (1:M)
- Many to one (M:1)
- Many to many (M:M)
One-to-one
In one-to-one mapping, an entity in E1 is associated with at most one entity in E2, and an entity in E2 is associated with at most one entity in E1.

One-to-many
In one-to-many mapping, an entity in E1 is associated with any number of entities in E2, and an entity in E2 is associated with at most one entity in E1.

Many-to-one
In one-to-many mapping, an entity in E1 is associated with at most one entity in E2, and an entity in E2 is associated with any number of entities in E1.

Many-to-many
In many-to-many mapping, an entity in E1 is associated with any number of entities in E2, and an entity in E2 is associated with any number of entities in E1.





No comments:
Post a Comment