The following are the functions which are widely used in computer science.
1. Floor Functions: The floor function for any real number x is defined as f (x) is the greatest integer 1 less than or equal to x. It is denoted by [x].
Example: Determine the value of
(i)[3. 5] (ii)[-2.4] (iii)[3. 143].
Solution:
(i)[3 . 5] = 3 (ii) [-2 .4] = -3 (iii) [3. 143] = 3
2. Ceiling Functions: The ceiling function for any real number x is defined as h (x) is the smallest integer greater than or equal to x. It is denoted by [x].
Example: Determine the value of
(i)[3. 5] (ii) [-2.4] (iii) [3. 143].
Solution:
(i)[3. 5] = 4 (ii) [-2 .4] = -2 (iii) [3. 143] = 4.
3. Remainder Functions: The integer remainder is obtained when some a is divided by m. It is denoted by a (MOD m). We can also define it as, a (MOD m) is the unique integer t such that a = Mq + t. Here q is quotient 0 ≤ r < M.
Example: Determine the value of the following:
(i) 35 (MOD 7) (ii) 20 (MOD 3) (iii) 4 (MOD 9)
Solution:
(i) 35 (MOD 7) = 0 (ii) 20 (MOD 3) = 2 (iii) 4 (MOD 9) = 4
4. Exponential Functions: Consider two sets A and B. Let A = B = I+ and also let f: A → B be defined by f (n) = kn. Here n is a +ve integer. The function f is called the base k exponential function.
Note1: kt= k. k. k.......k (t times).
2: k0=1,k-M=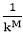
3. For rational number, a/b, the exponential function is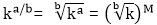
Example: Determine the value of the following:
(i) 103 (ii) 51/2 (iii) 3-5
Solution:
103= 10. 10. 10 = 1000 51/2=2.23607 3-5=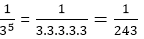
5. Logarithmic Functions: Consider two sets A and B. Let A = B = R (the set of real numbers and also let f_n:A→B be defined for each positive integer n > 1 as fn (x)=logn(x) the base n of x.
Note1: k = logn x and nk are equivalent.
2. For any base n, logn 1=0 as n0=1.
3. For any base n, logn n=1 as n1=n.
Example: Determine the value of the following:
(i) log2?16 (ii) log2 100 (iii) log_2 0.001.
Solution:
(i)log216 = 4 as 24=16. (ii)log2 100 = 6 as 26= 64 but 27=128 which is greater (iii)log2 0.001=-9 as 2-9=but 2-10=
which is greater.




No comments:
Post a Comment